The Ultimate Guide to Barcode Scanners: Revolutionizing Business Efficiency

In today’s fast-paced business environment, companies are constantly seeking ways to improve their operations, reduce errors, and enhance customer satisfaction. One of the most effective tools in achieving these goals is the barcode scanner. These devices have transformed various industries by facilitating quicker data entry, automating inventory management, and improving overall workflow efficiency. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the significance of barcode scanners, their types, applications in different business sectors, and how they can be integrated into your operations at Durafastlabel.ca.
Understanding Barcode Scanners
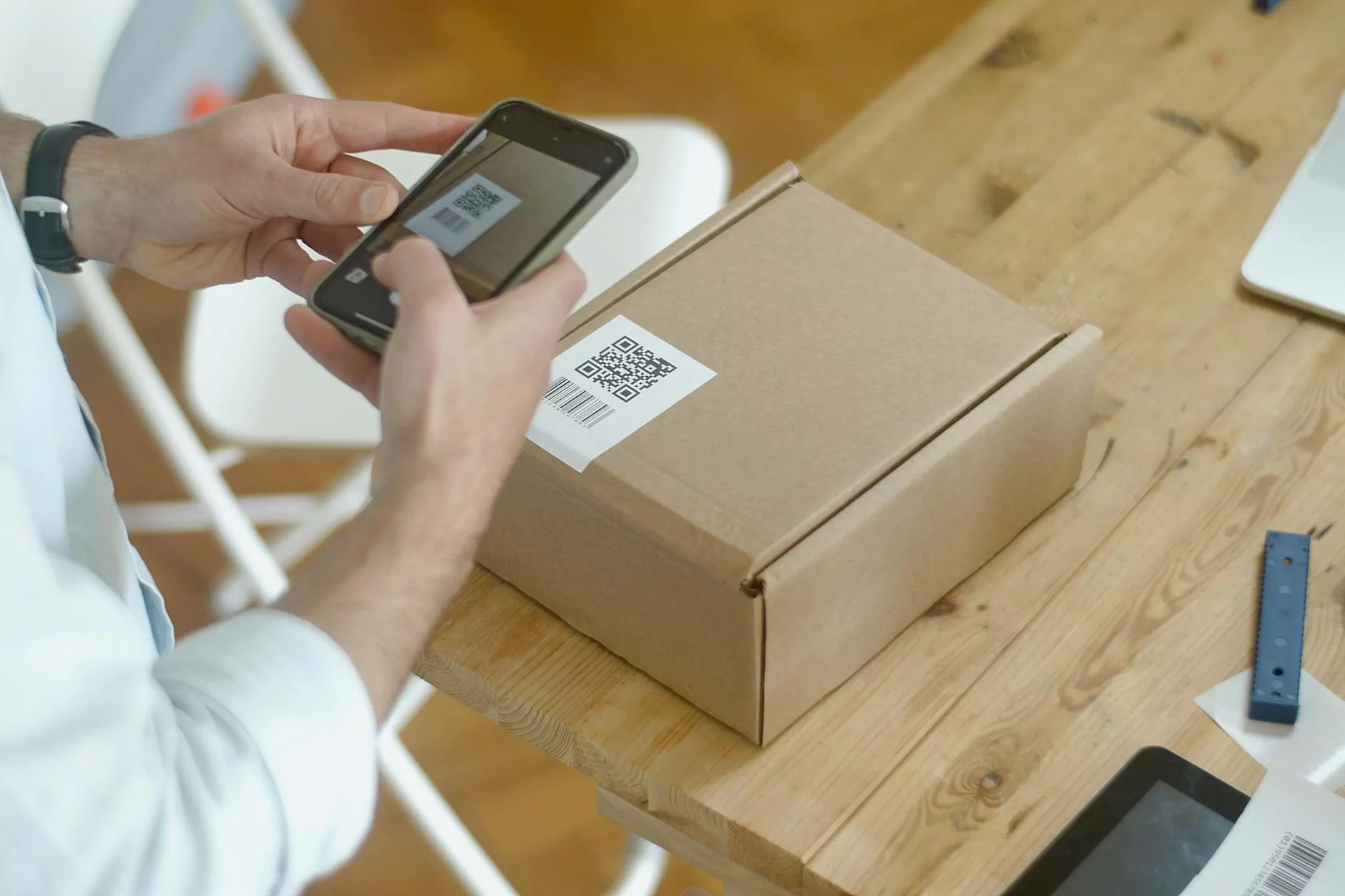
A barcode scanner is an electronic device that reads barcodes—visual representations of data in a series of varying-width lines and spaces. By scanning these codes, the device decodes the information, enabling businesses to track products, manage inventory, and provide streamlined customer service. In essence, barcode scanners serve as a bridge between physical items and digital data, making it easier to store, organize, and retrieve information.
The Importance of Barcode Scanners in Modern Business
The integration of barcode scanners in business operations is crucial for several reasons:
- Improved Accuracy: Manual data entry is prone to human error, whereas barcode scanners offer high levels of accuracy in tracking and managing products.
- Increased Efficiency: Scanning barcodes is significantly faster than typing information, allowing employees to focus on more productive tasks.
- Real-Time Inventory Management: Barcode scanners facilitate real-time data updates, enabling businesses to maintain accurate inventory levels, reduce shrinkage, and avoid stockouts.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Faster checkout processes and accurate product information lead to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Types of Barcode Scanners
There are several types of barcode scanners available in the market, each designed for specific applications and environments:
1. Handheld Barcode Scanners
Handheld scanners are portable devices, allowing for flexibility in scanning items in various locations. They are often used in retail environments or warehouses where mobility is required.
2. Fixed Mount Scanners
These scanners are mounted in a fixed location, making them ideal for assembly lines or checkout counters. They can scan items automatically as they pass by, streamlining the process.
3. Mobile Computers
Mobile computers are handheld devices equipped with a barcode scanner, a keypad, and a display. They are used for field operations and can store data for later synchronization with central systems.
4. Stationary Scanners
Stationary scanners are designed to remain in one place and usually interface with a computer or point of sale system. They are typically used in retail settings for fast checkout processes.
5. 2D Barcode Scanners
These scanners read both traditional 1D barcodes and 2D codes like QR codes. They are increasingly popular due to the rise of mobile marketing and ticketing.
Common Applications of Barcode Scanners
Barcode scanners are versatile tools, applicable across various sectors. Here are some key areas where businesses can leverage the benefits of barcode technology:
1. Retail
In the retail sector, barcode scanners are used for inventory management, point of sale systems, and loss prevention. They allow for quick scanning of products at checkout, reducing lines and improving the shopping experience.
2. Warehousing and Logistics
In warehouses, barcode scanners play an essential role in tracking stock levels, managing shipments, and ensuring the accurate movement of goods. They help automate receiving and shipping processes, reducing labor costs and errors.
3. Manufacturing
Manufacturers utilize barcode scanning to monitor production lines, manage materials, and track product quality. This real-time data collection enhances operational efficiency and ensures compliance with industry standards.
4. Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, barcode scanners streamline patient care by tracking medications, lab samples, and inventory supplies. They improve patient safety by ensuring that the correct medications are administered at the right times.
5. Transportation
Transportation companies rely on barcode scanners to track shipments and ensure timely deliveries. They provide information on package locations and estimated delivery times, enhancing customer satisfaction.
Choosing the Right Barcode Scanner for Your Business
When selecting a barcode scanner for your business, consider the following factors:
1. Type of Barcode
Determine which types of barcodes you will be scanning (1D or 2D) and choose a scanner that can accommodate these formats.
2. Environment
Consider where the scanner will be used. For rugged environments, choose durable models that can withstand drops and exposure to dust and moisture.
3. Connectivity
Assess how the scanners will connect to your existing systems. Wireless options provide flexibility, while wired options may offer faster data transfer rates.
4. Volume of Scanning
Estimate the volume of scanning needs. High-volume environments may require faster, more robust scanners to keep up with demands.
5. Budget
Determine your budget for barcode scanners, considering the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and operational costs.
How to Integrate Barcode Scanners with Your Business Systems
Integrating barcode scanners into your existing business systems involves several steps:
1. Assess Business Needs
Identify your specific requirements for barcode scanning. Know what processes you want to improve and how scanning can help.
2. Choose the Right Software
Select software that can efficiently manage inventory and integrate with your existing systems. Ensure it is compatible with the barcode scanners you plan to use.
3. Training Employees
Provide comprehensive training to staff on how to use the scanners and the associated software. This will help maximize efficiency and minimize errors.
4. Testing and Implementation
Conduct pilot tests to troubleshoot any issues before full-scale implementation. Gather feedback from users and make necessary adjustments.
5. Monitor Performance
After implementation, regularly monitor performance metrics to assess the effectiveness of the barcode scanning system. Make improvements as needed to optimize operations.
Future Trends in Barcode Scanning Technology
The future of barcode scanners is promising, with advancements poised to enhance their capabilities:
1. Mobile Scanning
The rise of smartphones has led to increased adoption of mobile scanning applications, turning personal devices into barcode scanners for businesses on the go.
2. Cloud Integration
Many businesses are adopting cloud-based systems, allowing for easier data access and management from any location. Barcode scanners will increasingly integrate with these cloud platforms.
3. Artificial Intelligence
AI will play a significant role in analyzing barcode data, providing insights for inventory predictions and improving supply chain management.
4. Enhanced Security Features
Next-generation barcode scanners will include advanced security features to protect sensitive data, especially in sectors like healthcare and finance.
Conclusion
Investing in a barcode scanner can significantly enhance your business operations, making them more efficient and less error-prone. By streamlining processes across various sectors—retail, logistics, manufacturing, and healthcare—your organization can improve productivity while delivering better customer service. At Durafastlabel.ca, we offer a range of printing services and electronic solutions, including high-quality barcode scanners tailored to fit your unique business needs. Explore the transformative power of barcode scanners today and position your business for success in an increasingly competitive marketplace.